4_自动装配与条件装配
自动装配与条件装配
解释摘自参考官网: Spring容器可以自动装配Beans之间的关系。可以让Spring通过检查
Application容器自动的解析合作者(其他Beans)
基于个官网的解释,我理解@Autowired是自动装配的一种实现。而@EnableAutoConfiguration、@ComponentScan是使用者,把目标对象纳入Spring容器管理。
即:条件装配是去人对象是否纳入Spring容器管理,在@EnableAutoConfiguration范围内。
自动装配具有以下优点:
- 自动装配可以显着减少指定属性或构造函数参数的需要。
- 随着对象的发展,自动装配可以更新配置。
自动装配限制和缺点:
自动装配在项目中一致使用时效果最佳。如果一般不使用自动装配,开发人员可能会混淆使用它来只装配一个或两个 bean 定义。
property和设置中的显示依赖constructor-arg项总是覆盖自动装配。不能自动装配简单的属性,例如:基础属性、String,Classes(和一些简单的properties数组)。此限制是设计使然- 自动装配不如显式装配精确。尽管如前表中所述,Spring 会小心避免猜测可能会产生意想不到的结果的歧义。Spring 管理的对象之间的关系不再明确记录。
- 从 Spring 容器生成文档的工具可能无法使用接线信息。
- 容器内的多个 bean 定义可能与要自动装配的 setter 方法或构造函数参数指定的类型匹配。对于数组、集合或
Map实例,这不一定是问题。但是,对于期望单个值的依赖项,这种歧义不会被任意解决。如果没有唯一的 bean 定义可用,则会引发异常。
最后一种情况,有多种选择:
- 放弃自动装配以支持显式装配。
autowire-candidate通过将其属性设置为 来避免对 bean 定义进行自动装配false,- 通过将其元素的
primary属性设置为true,将单个bean定义指定为主要的候选者- 使用基于注解的配置实现更细粒度的控制
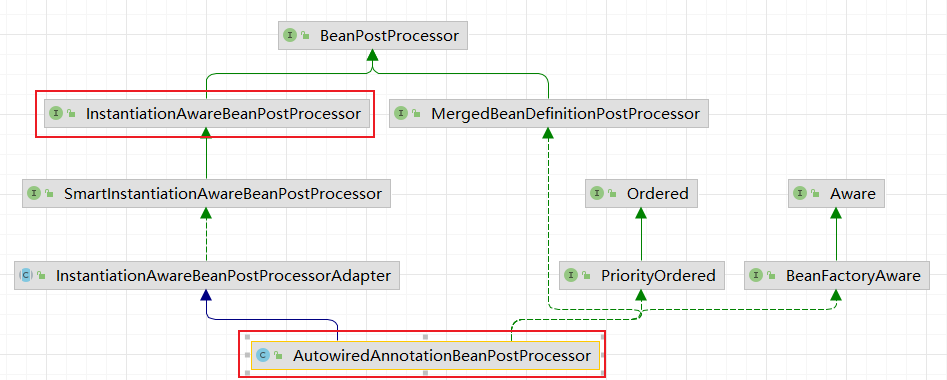
注解@Autowired
在Bean加载过程中,AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor对注解进行处理
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类实现了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors接口
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {
// 获取注解对应的元数据
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
try {
// 开始注入
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of autowired dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
}获取注解对应元数据
private InjectionMetadata findAutowiringMetadata(String beanName, Class<?> clazz, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) {
// 类名作为缓存键,以便与自定义调用者向后兼容
String cacheKey = (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) ? beanName : clazz.getName());
// 从缓存中获取,尽可能来减少获取数量
InjectionMetadata metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
// 有可能没有获取到,有可能已经被改变了都重新获取
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
synchronized (this.injectionMetadataCache) {
// 再取一次防止在取到后加上锁之前这条数据发生了改变的情况
metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
if (metadata != null) {
// 先清空
metadata.clear(pvs);
}
// 重新建立注入元数据
metadata = buildAutowiringMetadata(clazz);
// 重新添加缓存
this.injectionMetadataCache.put(cacheKey, metadata);
}
}
}
return metadata;
}建立注入元数据,AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor里的2个子类重写了inject()方法。分别负责字段的注入和方法的注入
字段的注入
private class AutowiredFieldElement extends InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement {
private final boolean required;
private volatile boolean cached = false;
@Nullable
private volatile Object cachedFieldValue;
public AutowiredFieldElement(Field field, boolean required) {
super(field, null);
this.required = required;
}
@Override
protected void inject(Object bean, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
// 取到目标类
Field field = (Field) this.member;
Object value;
if (this.cached) {
value = resolvedCachedArgument(beanName, this.cachedFieldValue);
}
else {
DependencyDescriptor desc = new DependencyDescriptor(field, this.required);
desc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());
Set<String> autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet<>(1);
Assert.state(beanFactory != null, "No BeanFactory available");
TypeConverter typeConverter = beanFactory.getTypeConverter();
try {
// 这里使用BeanFactory的resolveDependency方法获取值
// SpringBoot这里使用的是DefaultListableBeanFactory的实现
// 根据descriptor的依赖类型解析出与descriptor所包装的对象匹配的候选Bean对象
value = beanFactory.resolveDependency(desc, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new UnsatisfiedDependencyException(null, beanName, new InjectionPoint(field), ex);
}
synchronized (this) {
if (!this.cached) {
if (value != null || this.required) {
this.cachedFieldValue = desc;
registerDependentBeans(beanName, autowiredBeanNames);
if (autowiredBeanNames.size() == 1) {
String autowiredBeanName = autowiredBeanNames.iterator().next();
if (beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(autowiredBeanName, field.getType())) {
this.cachedFieldValue = new ShortcutDependencyDescriptor(
desc, autowiredBeanName, field.getType());
}
}
}
else {
this.cachedFieldValue = null;
}
this.cached = true;
}
}
}
if (value != null) {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
field.set(bean, value);
}
}
}方法的注入
打差不差,变成循环了
private class AutowiredMethodElement extends InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement {
private final boolean required;
private volatile boolean cached = false;
@Nullable
private volatile Object[] cachedMethodArguments;
public AutowiredMethodElement(Method method, boolean required, @Nullable PropertyDescriptor pd) {
super(method, pd);
this.required = required;
}
@Override
protected void inject(Object bean, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
if (checkPropertySkipping(pvs)) {
return;
}
Method method = (Method) this.member;
Object[] arguments;
if (this.cached) {
// Shortcut for avoiding synchronization...
arguments = resolveCachedArguments(beanName);
}
else {
int argumentCount = method.getParameterCount();
arguments = new Object[argumentCount];
DependencyDescriptor[] descriptors = new DependencyDescriptor[argumentCount];
Set<String> autowiredBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(argumentCount);
Assert.state(beanFactory != null, "No BeanFactory available");
TypeConverter typeConverter = beanFactory.getTypeConverter();
for (int i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
MethodParameter methodParam = new MethodParameter(method, i);
DependencyDescriptor currDesc = new DependencyDescriptor(methodParam, this.required);
currDesc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());
descriptors[i] = currDesc;
try {
// 获取对象
Object arg = beanFactory.resolveDependency(currDesc, beanName, autowiredBeans, typeConverter);
if (arg == null && !this.required) {
arguments = null;
break;
}
arguments[i] = arg;
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new UnsatisfiedDependencyException(null, beanName, new InjectionPoint(methodParam), ex);
}
}
synchronized (this) {
if (!this.cached) {
if (arguments != null) {
DependencyDescriptor[] cachedMethodArguments = Arrays.copyOf(descriptors, arguments.length);
registerDependentBeans(beanName, autowiredBeans);
if (autowiredBeans.size() == argumentCount) {
Iterator<String> it = autowiredBeans.iterator();
Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
for (int i = 0; i < paramTypes.length; i++) {
String autowiredBeanName = it.next();
if (beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(autowiredBeanName, paramTypes[i])) {
cachedMethodArguments[i] = new ShortcutDependencyDescriptor(
descriptors[i], autowiredBeanName, paramTypes[i]);
}
}
}
this.cachedMethodArguments = cachedMethodArguments;
}
else {
this.cachedMethodArguments = null;
}
this.cached = true;
}
}
}
if (arguments != null) {
try {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method);
method.invoke(bean, arguments);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw ex.getTargetException();
}
}
}
@Nullable
private Object[] resolveCachedArguments(@Nullable String beanName) {
Object[] cachedMethodArguments = this.cachedMethodArguments;
if (cachedMethodArguments == null) {
return null;
}
Object[] arguments = new Object[cachedMethodArguments.length];
for (int i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
arguments[i] = resolvedCachedArgument(beanName, cachedMethodArguments[i]);
}
return arguments;
}
}DefaultListableBeanFactory的resolveDependency()方法
descriptor -- 描述符的意思
public Object resolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String requestingBeanName,
@Nullable Set<String> autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException {
// 获取工厂的参数名发现器,设置到descriptor中
descriptor.initParameterNameDiscovery(getParameterNameDiscoverer());
// 【当descriptor的依赖类型是Optional时】
if (Optional.class == descriptor.getDependencyType()) {
// 创建Optional类型的符合descriptor要求的候选Bean对象并返回 出去
return createOptionalDependency(descriptor, requestingBeanName);
}
// 【当decriptord的依赖类型是ObjectFactory或者是ObjectProvider】
else if (ObjectFactory.class == descriptor.getDependencyType() ||
ObjectProvider.class == descriptor.getDependencyType()) {
// 新建一个 DependencyObjectProvider的实例并返回出去
return new DependencyObjectProvider(descriptor, requestingBeanName);
}
// 【当decriptord的依赖类型是javax.inject.Provider】
else if (javaxInjectProviderClass == descriptor.getDependencyType()) {
// 新建一个专门用于构建 javax.inject.Provider对象的工厂来构建创建Jse330Provider对象
return new Jsr330Factory().createDependencyProvider(descriptor, requestingBeanName);
}
else {
// 【当descriptor需要延迟加载时】
Object result = getAutowireCandidateResolver().getLazyResolutionProxyIfNecessary(
descriptor, requestingBeanName);
if (result == null) {
// 【当现在就需要得到候选Bean对象时】
// 如果result为null,即表示现在需要得到候选Bean对象,解析出与descriptor所包装的对象匹配 的候选Bean对象
result = doResolveDependency(descriptor, requestingBeanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
}
return result;
}
}doResolveDependency()方法:解析出与descriptor所包装的对象匹配的候选Bean对象
public Object doResolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Set<String> autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException {
// 设置新的当前切入点对象,得到旧的当前切入点对象
InjectionPoint previousInjectionPoint = ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(descriptor);
try {
// 尝试使用descriptor的快捷方法得到最佳候选Bean对象
Object shortcut = descriptor.resolveShortcut(this);
if (shortcut != null) {
return shortcut;
}
// 获取descriptor的依赖类型
Class<?> type = descriptor.getDependencyType();
// 尝试使用descriptor的默认值作为最佳候选Bean对象,使用此BeanFactory的自动装配候选解析器获取descriptor的默认值
Object value = getAutowireCandidateResolver().getSuggestedValue(descriptor);
if (value != null) {
// 如果value是String类型
if (value instanceof String) {
// 解析嵌套的值
String strVal = resolveEmbeddedValue((String) value);
// 获取beanName的合并后RootBeanDefinition
BeanDefinition bd = (beanName != null && containsBean(beanName) ?
getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName) : null);
value = evaluateBeanDefinitionString(strVal, bd);
}
TypeConverter converter = (typeConverter != null ? typeConverter : getTypeConverter());
try {
// 将value转换为type的实例对象并返回出去
return converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getTypeDescriptor());
}
catch (UnsupportedOperationException ex) {
// 如果descriptor有包装成员属性,根据descriptor包装的成员属性来将值转换为type然后返回出去
// 否则,根据descriptor包装的方法参数对象来将值转换为type然后返回出去
return (descriptor.getField() != null ?
converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getField()) :
converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getMethodParameter()));
}
}
// 尝试针对desciptor所包装的对象类型是[stream,数组,Collection类型且对象类型是接口,Map]的情况进行解析与依赖类型匹配的候选Bean对象
Object multipleBeans = resolveMultipleBeans(descriptor, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
if (multipleBeans != null) {
return multipleBeans;
}
// 尝试与type匹配的唯一候选bean对象,查找与type匹配的候选bean对象,构建成Map
Map<String, Object> matchingBeans = findAutowireCandidates(beanName, type, descriptor);
if (matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
if (isRequired(descriptor)) {
raiseNoMatchingBeanFound(type, descriptor.getResolvableType(), descriptor);
}
return null;
}
// 定义用于存储唯一的候选Bean名变量
String autowiredBeanName;
// 定义用于存储唯一的候选Bean对象变量
Object instanceCandidate;
// 如果候选Bean对象Map不止有一个
if (matchingBeans.size() > 1) {
// 让autowiredBeanName引用candidates中可以自动注入的最佳候选Bean名称
autowiredBeanName = determineAutowireCandidate(matchingBeans, descriptor);
if (autowiredBeanName == null) {
if (isRequired(descriptor) || !indicatesMultipleBeans(type)) {
return descriptor.resolveNotUnique(descriptor.getResolvableType(), matchingBeans);
}
else {
// In case of an optional Collection/Map, silently ignore a non-unique case:
// possibly it was meant to be an empty collection of multiple regular beans
// (before 4.3 in particular when we didn't even look for collection beans).
return null;
}
}
instanceCandidate = matchingBeans.get(autowiredBeanName);
}
else {
// We have exactly one match.
Map.Entry<String, Object> entry = matchingBeans.entrySet().iterator().next();
autowiredBeanName = entry.getKey();
instanceCandidate = entry.getValue();
}
if (autowiredBeanNames != null) {
// 如果候选bean名不为null,将autowiredBeanName添加到autowiredBeanNames中
autowiredBeanNames.add(autowiredBeanName);
}
// 如果instanceCandidate是Class实例
if (instanceCandidate instanceof Class) {
// 让instanceCandidate引用 descriptor对autowiredBeanName解析 为该工厂的Bean实例
// getBean()的封装,里面就是getBean()
instanceCandidate = descriptor.resolveCandidate(autowiredBeanName, type, this);
}
// 定义一个result变量,用于存储最佳候选Bean对象
Object result = instanceCandidate;
if (result instanceof NullBean) {
if (isRequired(descriptor)) {
raiseNoMatchingBeanFound(type, descriptor.getResolvableType(), descriptor);
}
result = null;
}
// 如果result不是type的实例,抛出Bean不是必需类型异常
if (!ClassUtils.isAssignableValue(type, result)) {
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(autowiredBeanName, type, instanceCandidate.getClass());
}
// 返回最佳候选Bean对象
return result;
}
finally {
ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(previousInjectionPoint);
}
}SpringBoot启动注解里@EnableAutoConfiguration
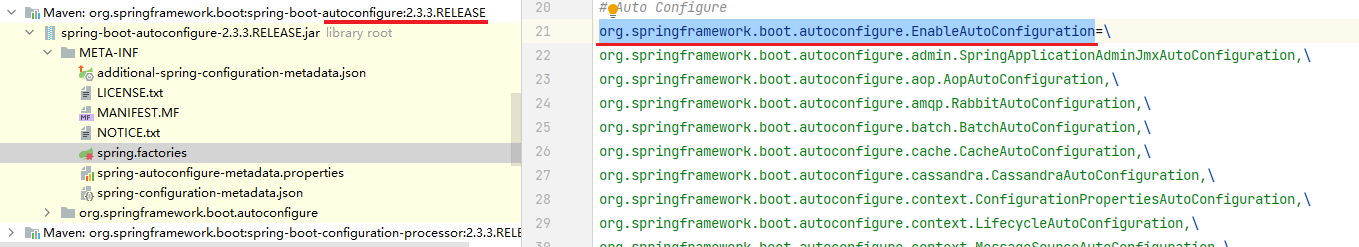
进入这个注解里最关键的要属@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class),借助AutoConfigurationImportSelector,@EnableAutoConfiguration注解可以帮助SpringBoot应用将所有符合条件的@Configuration配置都加载到当前SpringBoot创建并使用的IoC容器。
借助于Spring框架原有的一个工具类:SpringFactoriesLoader的支持,@EnableAutoConfiguration可以智能的自动配置功效才得以大功告成!
AutoConfigurationImportSelector的一部分:
这里这个AutoConfigurationImportSelector实现了DeferredImportSelector,这个类继承ImportSelect
而 AutoConfigurationImportSelector重写了selectImports 方法,这个方法把String[]里的内容装载进Spring容器里
// spring-boot-autoconfigure:2.3.3RELEASE版本如下:
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return NO_IMPORTS;
}
AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata);
return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations());
}
//spring-boot-autoconfigure2.0.5RELEASE如下,跟上面版本不一样。所以这里直接进入getCandidateConfigurations这个方法
// 把getAutoConfigurationEntry方法放在了selectImports里,这么一看猜测上面的版本更新
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return NO_IMPORTS;
}
AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader
.loadMetadata(this.beanClassLoader);
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata,
attributes);
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
configurations = filter(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata);
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return StringUtils.toStringArray(configurations);
}spring-boot-autoconfigure:2.3.3RELEASE版本再向下进到getAutoConfigurationEntry()
protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return EMPTY_ENTRY;
}
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
// 这里再向下就可以看到SpringFactoriesLoader
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
configurations = getConfigurationClassFilter().filter(configurations);
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return new AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions);
}进入getCandidateConfigurations()
/**
* Return the auto-configuration class names that should be considered. By default
* this method will load candidates using {@link SpringFactoriesLoader} with
* {@link #getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass()}.
* @param metadata the source metadata
* @param attributes the {@link #getAttributes(AnnotationMetadata) annotation
* attributes}
* @return a list of candidate configurations
*/
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
// getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass()返回的是 EnableAutoConfiguration.class
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(),
getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you "
+ "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}在AutoConfigurationImportSelector类中可以看到通过 SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(),这一步会把所有的 META-INF/spring.factories 都拿到放在一个map里(从代码中我们可以知道,在这个方法中会遍历整个ClassLoader中所有jar包下的spring.factories文件。也就是说我们可以在自己的jar中配置spring.factories文件,不会影响到其它地方的配置,也不会被别人的配置覆盖。)。loadFactoryNames()方法是从META-INF/spring.factories 形成的map里取出名称为“org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration”的列表。然后把spring-boot-autoconfigure.jar/META-INF/spring.factories中每一个xxxAutoConfiguration文件都加载到容器中。
通用格式是: 接口(或者注解)全类名=\接口实现类(或者使用了该注解的类)全类名-1,\接口实现类(或者使用了该注解的类)全类名-2,\...接口实现类(或者使用了该注解的类)全类名-n。
spring.factories中最常用的注解是org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration,通过配置此注解对应的实现了,底层会由AutoConfigurationImportSelector对响应的目标类进行加载和自动注册。通过阅读Spring Boot 3.0 Migration Guide得知,spring.factories功能在Spring Boot 2.7已经废弃,在Spring Boot 3.0移除。
列举其中一个例子:
如源码:
/**
* Load the fully qualified class names of factory implementations of the
* given type from {@value #FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION}, using the given
* class loader.
* 翻译:使用给定的类加载器从“ META-INF / spring.factories”加载给定类型的工厂实现的标准类名
* @param factoryType the interface or abstract class representing the factory
* @param classLoader the ClassLoader to use for loading resources; can be
* {@code null} to use the default
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if an error occurs while loading factory names
* @see #loadFactories
*/
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
// 从“ META-INF / spring.factories”形成的map里取出名称为“org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration”
//的列表
return loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}
/**
*这一步会把所有的“ META-INF / spring.factories”都拿到放在一个map里
*/
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = (MultiValueMap)cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
} else {
try {
// 获取所有spring.factories的URL
Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources("META-INF/spring.factories") : ClassLoader.getSystemResources("META-INF/spring.factories");
LinkedMultiValueMap result = new LinkedMultiValueMap();
while(urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = (URL)urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
Iterator var6 = properties.entrySet().iterator();
while(var6.hasNext()) {
Entry<?, ?> entry = (Entry)var6.next();
String factoryTypeName = ((String)entry.getKey()).trim();
String[] var9 = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String)entry.getValue());
int var10 = var9.length;
for(int var11 = 0; var11 < var10; ++var11) {
String factoryImplementationName = var9[var11];
result.add(factoryTypeName, factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
} catch (IOException var13) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [META-INF/spring.factories]", var13);
}
}
}spring.factories这个文件不是只是一个文件
META-INF/spring.factories这个文件不是只是一个文件,每个start都有一个
spring.factories被移除后的替代方案
Spring Boot 2.x升级到Spring Boot 3.0其实是一个"破坏性"升级,目前来看相对较大的影响是:
- 必须使用
JDK17 Jakarta EE的引入,导致很多旧的类包名称改变- 部分类被彻底移除
spring-data模块的所有配置属性必须使用spring.data前缀,例如spring.redis.host必须更变为spring.data.redis.hostspring.factories功能在Spring Boot 2.7已经废弃,在Spring Boot 3.0彻底移除(见下图)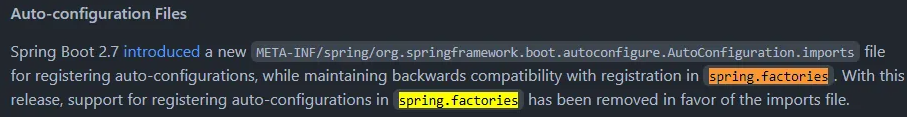
替代方案比较简单,就是在类路径下创建META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports文件,文件的内容是:每个实现类的全类名单独一行。 例如对于使用了(低版本还没适配Spring Boot 3.0)mybatis-plus、dynamic-datasource组件的场景,可以在项目某个模块的resources目录下建立META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports文件, 输入以下内容:
com.baomidou.dynamic.datasource.spring.boot.autoconfigure.DynamicDataSourceAutoConfiguration
com.baomidou.mybatisplus.autoconfigure.MybatisPlusLanguageDriverAutoConfiguration
com.baomidou.mybatisplus.autoconfigure.MybatisPlusAutoConfiguration注解@CompanentScan
会自动扫描包路径下面的所有@Controller、@Service、@Repository、@Component 的类
它里面的属性: value指定扫描的包,includeFilters包含那些过滤,excludeFilters不包含那些过滤,useDefaultFilters默认的过滤规则是开启的,如果我们要自定义的话是要关闭的。其中@Filters是一个过滤器的接口。
@Filters 指过滤规则,FilterType指定过滤的规则(
FilterType.ANNOTATION:按照注解
FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE:按照给定的类型;
FilterType.ASPECTJ:使用ASPECTJ表达式
FilterType.REGEX:使用正则指定
FilterType.CUSTOM:使用自定义规则)
classes指定过滤的类