堆排序
2025/8/16...大约 2 分钟
堆排序
堆排序是依赖堆的特性完成的排序。
堆分为小顶堆和大顶堆,堆是满二叉树结构且每个节点都是这个节点子树的最大或最小值,这样的结构为堆。根节点大的为大根堆,根节点为小的为小根堆。
堆排序,首先将数组映射成一个堆结构。可以映射成堆结构的原因是:数组的每个位置可以映射到堆的每个节点上。
排序原理:
我们现将数组的每个元素构造成大顶堆,然后逐个将堆顶与堆底交换,然后将堆底从堆中移除,重新维护大顶堆结构。周而复始可以将每个元素排好序。
如下图可以直观的感受数组和堆结构位置的映射关系
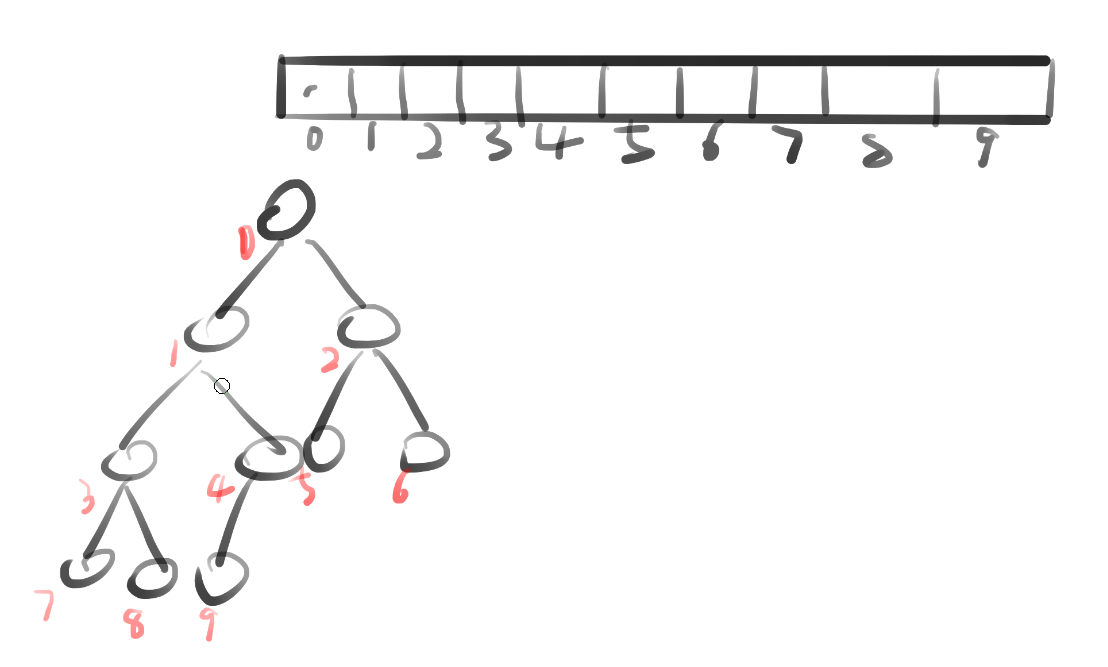
可以看到,重点的就是堆结构的维护。
插入:比较当前节点的父节点大小,比父节点大交换,直到不比父节点大或到达堆顶
更新:与两个子节点大的数比较,如果比节点小交换,直到比两个子节点都大或到达叶子节点
代码实现
package learn.note.algorithm.sort.three;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class HeapSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] list = new int[]{9,28,43,50,76,90,86,94,94,97};
heapSort(list);
// 对数器
CompareMachineUtil.compare(HeapSort::heapSort, null);
Arrays.stream(list).forEach(System.out::println);
}
private static void heapSort(int[] list) {
if (list == null || list.length <= 1) {
return;
}
int heapIndex = 0;
// 构建大顶堆
for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
heapInsert(list, heapIndex++);
}
// 将最后一个与从大顶堆堆顶交换,断掉最后一个与堆的联系。重新维护大顶堆
while (heapIndex > 0) {
swap(list, --heapIndex, 0);
heapify(list, 0, heapIndex);
}
}
private static void heapify(int[] list, int index, int heapIndex) {
int left = index * 2 + 1;
while (left < heapIndex) {
int largest;
if (left + 1 >= heapIndex) {
// 只有一个孩子
largest = left;
} else {
// 俩孩子比较大小
largest = list[index * 2 + 1] > list[index * 2 + 2] ? index * 2 + 1 : index * 2 + 2;
}
largest = list[largest] > list[index] ? largest : index;
if (largest == index) {
break;
}
swap(list, largest, index);
index = largest;
left = index * 2 + 1;
}
}
private static void heapInsert(int[] list, int heapIndex) {
// 这里要减一
while (list[heapIndex] > list[(heapIndex - 1) / 2]) {
swap(list, heapIndex, (heapIndex - 1) / 2);
heapIndex = (heapIndex - 1) / 2;
}
}
private static void swap(int[] list, int i, int j) {
int temp = list[i];
list[i] = list[j];
list[j] = temp;
}
}